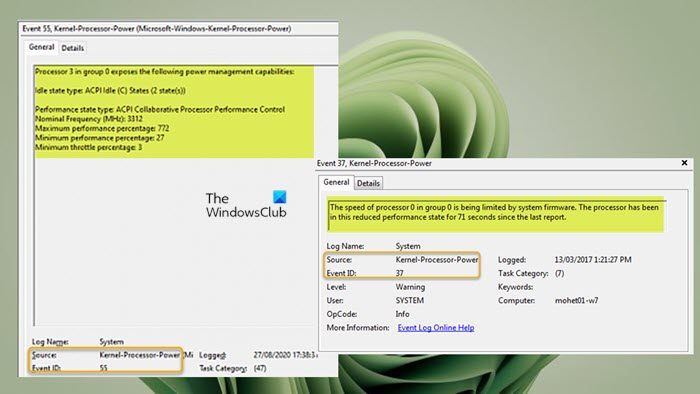
When this event is triggered and logged in Event Viewer, under the General tab, you may see a description along the following similar lines: OR Idle state type: ACPI Idle (C) States (2 state(s)) Performance state type: ACPI Collaborative Processor Performance ControlNominal Frequency (MHz): 3312Maximum performance percentage: 772Minimum performance percentage: 24Minimum throttle percentage: 3 Event ID: 55 Investigations revealed that this event is related to the power management of the processor on your computer. The event is generated when the system experiences an issue with the power management of the processor. This could be caused by a variety of factors, including hardware issues, driver issues, or problems with the power settings on your computer. Event ID: 37
Fix Event ID 55 (Kernel-Processor-Power) error
If the Event ID 55 or 37 (Kernel-Processor-Power) error is being logged in Event Viewer on your Windows 11/10 PC after exhibiting unusual behavior like the hard disk automatically shutting down when in use after a couple of minutes, then our suggested fixes presented below can be applied to resolve the issue. Let’s have a look at these recommended fixes in detail.
1] Initial checklist
Complete each task listed below, and after each task, continue using your PC normally and see if the issue reoccurs or if you notice any symptoms or abnormal PC behavior before the issue starts; then perform the next task.
Turn off Fast Startup in Power Options and disable Fast Boot in BIOS/UEFI.Run the SFC/DISM scan.Uninstall Windows update or roll back Windows upgrade as the case may be.Use the System Restore feature to revert your system to an earlier point in time before you started noticing the issue.If you have overclocked your CPU, you can revert the CPU to the default manufacturer setting by uninstalling the overclocking software or looking for the option to disable the overclocking in the software settings in use. In addition, you can use the utility ThrottleStop to monitor & disable CPU throttling that laptop computers especially are sometimes subjected to – a series of events that could lead to a system freeze, chokes, and even complete shutdown which may be the case here.Run the Hardware and Devices Troubleshooter just in case and use the utility OCCT to test for PSU issues (applies to Desktop PCs).Troubleshoot in Clean Boot state.
2] Run the Power Troubleshooter
You can run the Power Troubleshooter which will detect and recommend appropriate steps you can take to fix any underlying power issues that might have triggered the event. Windows 11
Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings app.Navigate to System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters.Under the Other section, find Power.Click the Run button.Follow on-screen instructions and apply any recommended fixes.
Windows 10
Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings app.Go to Update and Security.Click the Troubleshooter tab.Scroll down and click on Power.Click the Run the troubleshooter button.Follow on-screen instructions and apply any recommended fixes.
In addition, if applicable, check to see if the Intel(R) SpeedStep Technology is installed on your Windows 11/10 computer or enabled in the BIOS. Also, in Windows, check your Power Options and make sure that your Power Plan is set to High Performance, and check that every option is set to Always On. And make sure that your power settings are set to maximum in your BIOS setting. Read: How to check the Shutdown and Startup Log in Windows
3] Configure power options for the hard disk
Suppose your computer automatically shuts down and either of the events is logged in Event Viewer on startup. In that case, it could be your hard disk is set to turn off after a particular period of idle time to save power – in which case, you need to configure the power options for your hard disk as follows:
Press Windows Key + S, and type power.Choose Power & sleep settings from the menu.When the Power Options window opens, click on Additional power settings.Find your current plan. If Power Plans are missing, you can restore them.Click on Change plan settings for your active power plan.On the Edit Plan Settings applet that opens, click on Change advanced power settings.In the Power Options panel that appears, scroll to the Hard disk section and click to expand.Next, click on Turn off hard disk after and set it to Never.Next. Click the Sleep section to expand.Select Sleep after and also set it to Never.Click Apply > OK to save the changes.Restart PC.
If, however, this isn’t the case, or the hard disk power settings tweak didn’t work to resolve the issue at hand, you can continue with the next solution. Read: Prevent Hard Disk from going to Sleep in Windows
4] Change the Maximum processor state
This solution requires you to manage processor usage for optimum power management on your Windows 11/10 computer by changing the maximum processor power state so that your CPU will run at maximum power all the time. To perform this task, follow these steps:
Access Power Options > Change plan settings > Change advanced power settings > Processor power management > Maximum processor state.Now, select 100% when it’s on both Battery and Plugged in.Next, expand the System cooling policy option, and make sure to set it as Active to ensure there will be no overheating.Once done, click Apply > OK to save changes.
Read: CPU is not running at full speed or capacity in Windows
5] Update BIOS and Chipset drivers
As it is likely you’re dealing with outdated firmware on your PC, you can make sure the BIOS is up to date and all the drivers are up to date as well – especially make sure to update the Chipset drivers as these drivers are software instructions that tell Windows how to properly communicate and work with your motherboard and the small subsystems on it, and are based on the processor family you can use on that motherboard. Read: Fix ACPI BIOS ERROR or ACPI BIOS FATAL ERROR in Windows
6] Contact PC hardware technician
If you are unable to resolve the issue on your own after applying the fixes presented in this post, there is a possibility that the processor itself is faulty. This might happen when the processor is overheating or getting low power from the motherboard or in the power supply. In this case, to further diagnose the issue, you may want to consider contacting a PC hardware technician. If it’s a new PC that is still covered by warranty, you may want to take advantage of that service. I hope this helps! Related post: Kernel-Power Event ID 41 Task 63 error in Windows
Is Kernel-Power serious?
If your PC shuts down unexpectedly such as out of power or your PC reboots, then you may encounter the Kernel-Power issue. The Kernel-Power critical error is a vital error that if left undiagnosed and resolved, could potentially trigger Windows instability. This critical error could be due to a bug that there is a fix ready for in an update. So, first, check for updates, and if there is an update waiting, download and install it, then restart your system. Read: Fix Kernel Power Bluescreen Error on Windows
What happens when a kernel crashes?
When a kernel crashes or in a kernel panic, the kernel terminates abnormally. In a system crash which is different from a kernel crash, the kernel forcefully terminates a software execution after detecting an abnormal condition to minimize data loss or corruption in the device. A kernel panic also stops all CPU operations. To restart operations, the OS reboots automatically or waits for the user to reboot manually.